Dictionary

Minimal Art
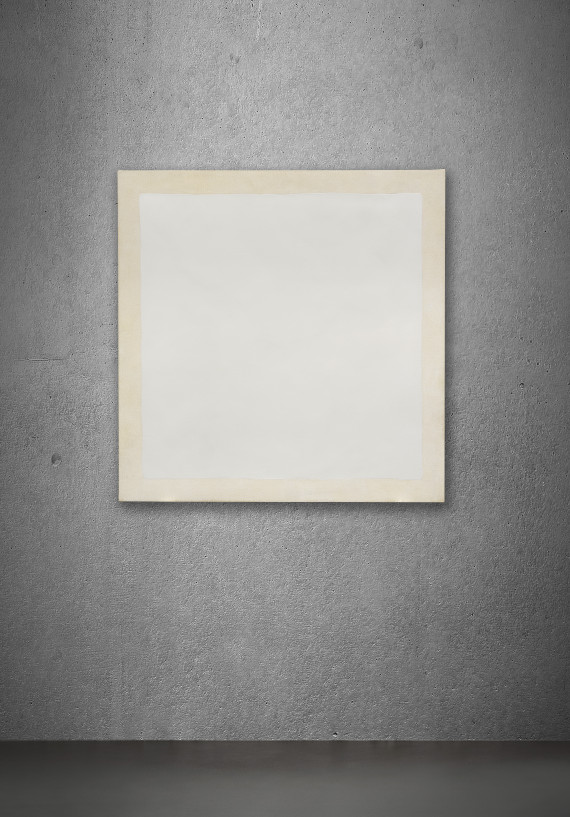
Minimal art was an artistic style, which emerged in America the late 1950s. The term was taken from an essay about modern American art by art philosopher Richard Wollheim in 1965. Hard Edge and Colour Field Painting tendencies were an important pre-requisite for the development of this style, as they had essentially prepared the ground for the use of very simple, reduced minimal forms. Minimal Art first established itself in painting, and then sculpture, where it had the greatest impact.
Minimal art sculptures were primarily made from industrial materials, such as aluminium, steel, glass, concrete, wood, plastic or stone. The objects, frequently reduced to very simple geometric shapes, were industrially produced, thus removing the artist’s personal signature from the work. The works were also characterised by serial arrangements of a number of bodies/shapes, and large dimensions.
The main representatives of Minimal art were Carl Andre, Dan Flavin, Donald Judd, Sol LeWitt, John McCracken and Robert Morris.
In contrast with Abstract Expressionism and its impulsive and gestural expression of the unconsciousness, Minimal artists focused on material aesthetics, the relationship of objects to space, the effects of light, and producing highly reduced arrangements. Donald Judd (1928-94) followed these basic principles, arranging coloured aluminium boxes in different ways, above, or next to one another. Carl Andre (born 1935) stacked rectangular wooden pegs on top of each other, or in a row. Dan Flavin (1933-96) created subtle light spaces with evenly laid out neon tubes. Minimalism also had an impact on dance and music in the 1960s. Minimalist principles also influenced artistic phenomenon such as Land Art, Arte Povera and Conceptual Art.
Minimal art was an artistic style, which emerged in America the late 1950s. The term was taken from an essay about modern American art by art philosopher Richard Wollheim in 1965. Hard Edge and Colour Field Painting tendencies were an important pre-requisite for the development of this style, as they had essentially prepared the ground for the use of very simple, reduced minimal forms. Minimal Art first established itself in painting, and then sculpture, where it had the greatest impact.
Minimal art sculptures were primarily made from industrial materials, such as aluminium, steel, glass, concrete, wood, plastic or stone. The objects, frequently reduced to very simple geometric shapes, were industrially produced, thus removing the artist’s personal signature from the work. The works were also characterised by serial arrangements of a number of bodies/shapes, and large dimensions.
The main representatives of Minimal art were Carl Andre, Dan Flavin, Donald Judd, Sol LeWitt, John McCracken and Robert Morris.
In contrast with Abstract Expressionism and its impulsive and gestural expression of the unconsciousness, Minimal artists focused on material aesthetics, the relationship of objects to space, the effects of light, and producing highly reduced arrangements. Donald Judd (1928-94) followed these basic principles, arranging coloured aluminium boxes in different ways, above, or next to one another. Carl Andre (born 1935) stacked rectangular wooden pegs on top of each other, or in a row. Dan Flavin (1933-96) created subtle light spaces with evenly laid out neon tubes. Minimalism also had an impact on dance and music in the 1960s. Minimalist principles also influenced artistic phenomenon such as Land Art, Arte Povera and Conceptual Art.
Offers for Conceptual art / Minimalism
Headquarters
Joseph-Wild-Str. 18
81829 Munich
Phone: +49 89 55 244-0
Fax: +49 89 55 244-177
info@kettererkunst.de
Louisa von Saucken / Undine Schleifer
Holstenwall 5
20355 Hamburg
Phone: +49 40 37 49 61-0
Fax: +49 40 37 49 61-66
infohamburg@kettererkunst.de
Dr. Simone Wiechers / Nane Schlage
Fasanenstr. 70
10719 Berlin
Phone: +49 30 88 67 53-63
Fax: +49 30 88 67 56-43
infoberlin@kettererkunst.de
Cordula Lichtenberg
Gertrudenstraße 24-28
50667 Cologne
Phone: +49 221 510 908-15
infokoeln@kettererkunst.de
Hessen
Rhineland-Palatinate
Miriam Heß
Phone: +49 62 21 58 80-038
Fax: +49 62 21 58 80-595
infoheidelberg@kettererkunst.de
We will inform you in time.